-
Introduction to Biological Classification
-
History of Biological Classification
-
Three and Four Kingdom Systems
-
Five Kingdom System
-
Three Domains of Life
-
History of Plant Classification
-
Kingdom Monera
-
Bacteria – Size, Shape and Arrangement
-
Bacterial Cell Envelope
-
Bacterial Cytoplasm
-
Bacterial Cell Surface Structures
-
Nutrition in Bacteria
-
Respiration in Bacteria
-
Reproduction in Bacteria
-
Archaebacteria: The Oldest Bacteria
-
Cyanobacteria: The Blue-Green Algae
-
Mycoplasma: The Wall-Less Bacteria
-
Gram Staining of Bacteria
-
Structure of Virus
-
Types of Viruses and Viral Diseases
-
Reproduction in Viruses
-
Viroids, Prions and Virusoids
-
Introduction to Kingdom Protista
-
Chrysophytes: The Golden Algae
-
Pyrrophytes: The Fire Algae
-
Euglenoids: The Photosynthetic Protists
-
Slime Moulds: The Saprophytic Protists
-
Protozoans: The Heterotrophic Protists
-
Flagellated Protozoans
-
Amoeba: The Amoeboid Protozoans
-
Amoeboid Protozoans and Their Orders
-
Sporozoans: The Parasitic Protozoans
-
Ciliated Protozoans
-
Kingdom Fungi
-
Vegetative and Asexual Reproduction in Fungi
-
Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
-
Types of Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
-
Classification of Fungi
-
Phycomycetes – Oomycetes and Zygomycetes
-
Importance and Diseases of Oomycetes and Zygomycetes
-
General Features of Ascomycetes
-
Importance of Ascomycetes
-
General Features Basidiomycetes
-
Importance of Basidiomycetes
-
General Features and Importance of Deuteromycetes
-
Lichens and Mycorrhiza
-
Introduction to Plant Kingdom
-
Thallophyta (Algae) – General Features and Importance
-
Rhodophyceae (Red Algae)
-
Examples and Importance of Red Algae
-
Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae)
-
Examples and Importance of Brown Algae
-
Chlorophyceae (Green Algae)
-
Examples of Green Algae – Chlamydomonas
-
Examples of Green Algae – Volvox
-
Examples of Green Algae – Ulothrix, Spirogyra and Chara
-
General Features of Bryophytes
-
Bryophytes – Liverworts (Marchantia)
-
Bryophytes – Mosses
-
General Features of Pteridophytes
-
Reproduction in Pteridophytes
-
Types of Pteridophytes
-
Importance of Pteridophytes
-
Pteridophytes – Selaginella
-
Difference Between Bryophytes and Pteridophytes
-
General Features of Gymnosperms
-
Reproduction in Gymnosperms
-
Types of Gymnosperms
-
General Features of Angiosperms
-
Life Cycle of Angiosperms
-
Problems on Plant Kingdom
-
Introduction to Morphology of Flowering Plants
-
Types and Regions of Roots
-
Modification of Roots
-
Stem of a Plant
-
Types of Stem
-
Modifications of Stem
-
Leaf of a Plant
-
Types of Venation in Leaves
-
Types of Leaves
-
Phyllotaxy: The Arrangement of Leaves
-
Modifications of Leaf
-
Inflorescence and Its Types
-
Racemose Inflorescence and Its Types
-
Cymose Inflorescence and Its Types
-
Special Inflorescence
-
General Description of a Flower
-
Floral Symmetry
-
Flower – Aestivation
-
Flower: Position of Ovary
-
Flower – Gynoecium
-
Flower – Calyx and Corolla
-
Ovules and Placentation
-
Flower – Androecium
-
Fruits and Their Types
-
Aggregate and Composite Fruits
-
Simple Fleshy Fruits
-
Simple Dry Fruits
-
Structure of Dicot and Monocot Seed
-
Floral Formula
-
Floral Diagram
-
Family Fabaceae
-
Family Solanaceae
-
Family Liliaceae
-
Introduction to Anatomy of Flowering Plants
-
Plant Meristematic Tissues
-
Apical Meristem
-
Intercalary and Lateral Plant Meristems
-
Simple Permanent Tissues – Parenchyma
-
Simple Permanent Tissues – Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma
-
Complex Permanent Tissues – Xylem
-
Complex Permanent Tissues – Phloem
-
Types of Xylem and Phloem
-
Epidermal Tissue System
-
Ground Tissue System
-
Vascular Tissue System
-
Structure of Dicot and Monocot Roots
-
Structure of Dicot Stem
-
Structure of Monocot Stem
-
Structure of Dicot Leaf
-
Structure of Monocot Leaf
-
Secondary Growth – Vascular Cambium
-
Secondary Growth – Cork Cambium
-
Spring Wood and Autumn Wood
-
Heartwood and Sapwood
-
Secondary Growth in Roots
-
Introduction to Animal Tissues
-
Main Features of Epithelial Tissues
-
Specialised Structures and Junctions
-
What Are Simple and Stratified Epithelial Tissues?
-
Squamous Epithelium
-
Cuboidal Epithelial Tissues
-
Columnar Epithelium
-
Pseudostratified and Transitional Epithelium
-
Glandular Epithelium
-
What Is Connective Tissue?
-
Cells of Connective Tissues
-
Fibres of Connective Tissue
-
Loose Connective Tissue – Areolar and Adipose
-
Dense Connective Tissue
-
Skeletal Connective Tissue – Cartilage
-
Skeletal Connective Tissue – Bones
-
Internal Structure of Bone
-
Differences Between Bone and Cartilage
-
What Are Muscle Tissues?
-
Striated or Skeletal Muscular Tissue
-
Unstriated or Smooth Muscular Tissue
-
Cardiac Muscular Tissue
-
Cells of the Nervous Tissue
-
Structure of a Nerve
-
Vascular Connective Tissue
-
Earthworm – Introduction and Body Wall
-
Earthworm – Morphology
-
Earthworm – Digestive System
-
Earthworm – Blood Vascular System
-
Earthworm – Respiratory and Excretory Systems
-
Earthworm – Reproduction
-
Earthworm – Nervous System and Economic Importance
-
Cockroach – Introduction and Body Wall
-
Cockroach – Morphology
-
Cockroach – Digestive System
-
Cockroach – Blood Vascular System
-
Cockroach – Respiratory and Excretory Functions
-
Cockroach – Nervous System
-
Cockroach – Reproductive System
-
Frog – Introduction, Morphology and Body Wall
-
Frog – Digestive, Respiratory and Blood Vascular Systems
-
Frog – Excretory, Nervous and Reproductive Systems
-
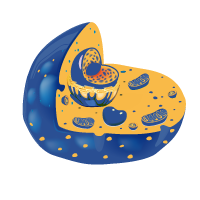
Introduction to Cell
-
Shape, Size and Types of Cells
-
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
-
Cell Membrane: The Outer Cover of the Cell
-
Membrane Transport – Passive Transport
-
Membrane Transport – Active Transport
-
Membrane Transport – Bulk Transport
-
Cytoplasm: The Ground Material of the Cell
-
The Endomembrane System and ER
-
Golgi Apparatus: The Post Office of the Cell
-
Lysosomes: The Suicidal Bags of the Cell
-
Vacuoles: The Storage Bodies of the Cell
-
Role of the Endomembrane System
-
Mitochondria: The Power House of the Cell
-
The Cytoplasmic Microbodies
-
Ribosomes: The Protein Factories of the Cell
-
Cytoskeleton – Microfilaments
-
Cytoskeleton – Intermediate Filaments
-
Cytoskeleton – Microtubules
-
Flagella and Cilia
-
Centrioles and Centrosome
-
Nucleus: The Brain of the Cell
-
Introduction to Chromosomes
-
Types of Chromosome
-
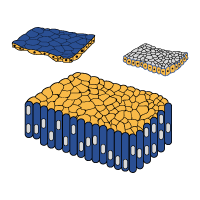
Introduction to Cell Wall
-
Structure of Cell Wall
-
Introduction to Plastids
-
Chloroplast: The Kitchen of the Cell
-
Differences Between Plant Cells and Animal Cells
-
Differences Between Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic Cells
-
Introduction to Biomolecules
-
Bonding in Biomolecules
-
Protein Monomers: The Amino Acids
-
Peptides and Protein Primary Structure
-
Secondary Protein Structure
-
Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Structures
-
Functions of Proteins
-
Carbohydrates: Classification and Function
-
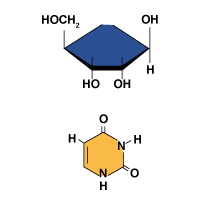
Carbohydrate Monomers: The Monosaccharides
-
Glycosidic Bond and Disaccharides
-
Polysaccharides: General Introduction and Types
-
Homopolysaccharides: Cellulose, Starch and Glycogen
-
Some Other Polysaccharides
-
Nucleic Acid Structure
-
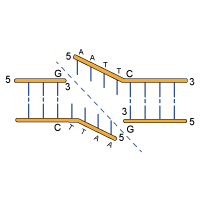
Structure of DNA
-
RNA and Its Types
-
Lipids: General Introduction and Function
-
Lipids Formation and Structure
-
Phospholipids, Sphingolipids and Glycolipids
-
Steroids and Lipoproteins
-
Enzymes and Their Properties
-
Nomenclature and Classification of Enzymes
-
How Do Enzymes Catalyse Reaction?
-
Models for Enzyme Action
-
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
-
Enzyme Inhibition
-
Cofactors and Coenzymes
-
Primary Metabolites and Secondary Metabolites
-
What Is Diffusion?
-
Facilitated Diffusion
-
Active Transport
-
Plant-Water Relations – Water Potential
-
Plant-Water Relations – Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure
-
Types of Solution and Plasmolysis
-
Turgor Pressure, Wall Pressure and Diffusion Pressure Deficit
-
Understanding Imbibition
-
Uniport, Symport and Antiport
-
Practice Questions on Plant-Water Relations
-
Symplast and Apoplast
-
Ascent of Sap – Root Pressure Theory
-
Transpiration – Types and Factors Affecting It
-
Ascent of Sap – Transpiration Pull or Cohesion-Tension Theory
-
Stomata – Structure and Types
-
Mechanism of Opening and Closing of Stomata
-
Uptake and Transport of Mineral Nutrients
-
Translocation Of Food in Plants By Phloem
-
Types of Water in Soil
-
Introduction to Mineral Nutrition
-
Mineral Requirements of Plants
-
Understanding Hydroponics
-
Essential Mineral Elements and Their Types
-
Role of Macronutrients
-
Role of Micronutrients – 1
-
Role of Micronutrients – 2
-
General Functions of Essential Elements
-
Deficiency Symptoms of Essential Elements
-
Toxicity of Micronutrients
-
Absorption of Minerals and Their Translocation
-
Soil: A Reservoir of Nutrients
-
Introduction to Nitrogen Cycle and Nitrogen Fixation
-
Nitrogen Cycle
-
Mechanism of Biological Nitrogen Fixation
-
Biochemistry of Nitrogen Fixation by Bacteria
-
Nitrate Assimilation in Plants
-
Introduction to Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
-
Early Experiments of Photosynthesis – Part I
-
Early Experiments of Photosynthesis – Part II
-
Action and Absorption Spectrum of Photosynthesis
-
Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
-
Photosynthetic Pigments
-
What Are Photosystems?
-
Emerson Effect
-
Z-Scheme and ETS in Light Reaction
-
Cyclic Photophosphorylation
-
Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation
-
Chemiosmotic Theory
-
Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
-
Photorespiration or C2 Cycle
-
C4 Pathway and C4 Plants
-
CAM Pathway
-
Blackman's Law of Limiting Factors
-
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
-
Introduction to Plant Growth and Development
-
Seed Germination in Plants
-
Plant Growth and Its Features
-
Methods To Measure Plant Growth
-
Phases of Plant Growth
-
Factors Affecting Plant Growth
-
Differentiation, Dedifferentiation, and Redifferentiation in Plants
-
Development in Plants
-
Meristematic Tissues and Plant Growth
-
Plant Growth Regulators
-
Discovery and Plant Growth Hormones
-
Plant Growth Hormones – Auxin
-
Plant Growth Hormones – Gibberellins
-
Differences Between Auxins and Gibberellins
-
Plant Growth Hormones – Cytokinin
-
Plant Growth Hormones – Ethylene and Abscisic Acid
-
Seed Dormancy and Its Importance
-
Interactions Among PGRs
-
Photoperiodism and Its Significance
-
Differences Between Short Day Plants and Long Day Plants
-
Vernalisation and Its Mechanism
-
Differences Between Vernalisation and Photoperiodism
-
Contents of the Oral Cavity
-
Salivary Glands and Their Contribution
-
Description of the Pharynx and the Oesophagus
-
Structure of Stomach
-
Small Intestine – Structure and Function
-
Intestinal Glands – Structure and Function
-
Large Intestine – Structure and Function
-
Structural Aspects of Liver
-
Functional Aspects of Liver
-
Bile: Liver's Key Factor
-
Pancreas – Structure and Function
-
The Biliary System
-
Gall Bladder: The Bile Storehouse
-
Pancreatic Juice – Constituents and Function
-
Carbohydrate Digestion
-
Protein Digestion
-
Fat Digestion
-
Absorption of Nutrients
-
Assimilation: Fate of Absorbed Food
-
Egestion: Expulsion of Unabsorbed Food
-
GIT Hormones
-
Deficiency Disorders
-
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
-
Water-Soluble Vitamins – B1, B2, B3, B5
-
Water-Soluble Vitamins – B6, B7, B9, B12, C
-
Motility and Disorders of the Digestive System
-
Intracellular Circulation and Extracellular Circulation
-
Blood – Components, Characteristics and Function
-
RBC – Formation, Structure and Function
-
Haemoglobin: The Respiratory Molecule
-
Granular Leucocytes
-
Agranular Leukocytes
-
Rh Blood Group
-
Blood Platelets
-
ABO Blood Grouping System
-
Circulatory Pathways
-
External Structure of Heart
-
Internal Structure of Heart
-
Lymph and Its Circulation
-
Lymphatic Organs
-
Cardiac Cycle, Stroke Volume, and Pulse
-
Cardiac Output and Heart Sounds
-
Understanding the Electrocardiograph
-
Blood Vessels
-
Double Circulation
-
Portal Circulation
-
Regulation of Cardiac Activity
-
Hypertension and Coronary Artery Disease
-
Anaemia, Haemophilia and Leukaemia
-
CHF, Cardiac Arrest and Arrhythmia
-
Angina, Congenital Heart Defects and Tetralogy of Fallot
-
Types of Movement
-
Properties and Functions of Muscular Tissue
-
Skeletal Muscle Fibre
-
Structure of Skeletal Muscle Fibre
-
Structure of Myofibril Proteins
-
Mechanism of Muscle Contraction and Relaxation
-
Muscle Potential at NMJ
-
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles
-
Smooth Muscle Tissue
-
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
-
Overview of the Skeletal System
-
Cranial and Facial Bones
-
Hyoid Bone and Ear Ossicles
-
Vertebral Column
-
Cervical and Thoracic Vertebrae
-
Lumbar, Sacrum and Coccyx
-
Thoracic Cage
-
Bones of the Upper Limb
-
Bones of the Lower Limb
-
Pectoral Girdle
-
Pelvic Girdle
-
Joints in the Human Body – I
-
Joints in the Human Body – II
-
Synovial Joints
-
Muscular Disorders – I
-
Muscular Disorders – II
-
Introduction to Neurons, Nerve Fibres and Neural Control and Coordination
-
Neural System in Animals
-
The Human Neural System – Classification and Functions
-
Structure of a Neuron
-
Classification of Neurons and Myelination
-
Neuroglia and Its Classification
-
Generation of Nerve Impulse
-
Conduction of Nerve Impulse
-
Understanding Synapses
-
What Is a Neurotransmitter?
-
Brain and Meninges
-
The Forebrain
-
Mibrain and Hindbrain
-
Spinal Cord and Ventricles
-
Cranial and Spinal Nerves
-
Divisions of PNS
-
Reflex Action
-
Sensory Receptors
-
Parts of an Eye
-
Anatomy of Eyeball
-
What Are Photoreceptors?
-
Vision – Mechanism and Abnormalities
-
External and Middle Ear
-
Anatomy of Inner Ear
-
Mechanism of Hearing
-
Tactile Sensation
-
Smell and Taste Sensations
-
Neural System Disorders
-
Neural vs Endocrine
-
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
-
Classification of Hormones
-
The Hypothalamus
-
Anterior Pituitary Gland – I
-
Anterior Pituitary Gland – II
-
Posterior Pituitary Gland
-
Pineal Gland
-
Thyroid Gland
-
Parathyroid Gland
-
Adrenal Gland – Cortex
-
Adrenal Gland – Medulla
-
Thymus Gland
-
Pancreas Gland
-
Understanding the Testes
-
Understanding the Ovary
-
Placenta, Liver and Heart Hormones
-
Kidney and GIT Hormones
-
Growth Factors and Eicosanoids
-
Mechanism of Action of Lipid-Soluble Hormones
-
Mechanism of Action of Water-Soluble Hormones
-
Regulation of Activity of Endocrine System
-
Disorders of Pituitary Gland and Gonads
-
Disorders of Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
-
Adrenal Gland Disorders
-
Pancreatic Islet Disorders
-
Structure of Stamen and Microsporangia
-
Anther Development and Microsporogenesis
-
Structure of Pollen Grains and Formation of Male Gametophyte
-
Structure of Pistil and Ovule or Megasporangium
-
Types of Ovules
-
Megasporogenesis and Embryo Sac Formation
-
Self-Pollination and Its Types
-
Cross-Pollination and Its Adaptation
-
Cross-Pollination: Part 1
-
Cross-Pollination: Part 2
-
Pollen-Pistil Interaction – Compatibility
-
Double Fertilisation and Triple Fusion
-
Endosperm and Its Types
-
Embryo Development in Dicots
-
Embryo Development in Monocots
-
Apomixis and Polyembryony
-
Introduction to Reproduction
-
Testes and Scrotal Sac
-
Seminiferous Tubules
-
Accessory Ducts
-
What Is Semen?
-
Accessory Sex Glands
-
Understanding Spermatogenesis
-
Spermiation, Capacitation and Factors Controlling Spermatogenesis
-
Structure of the Penis and Sperm
-
Ovary – The Primary Female Sex Organ
-
The Womb (Uterus)
-
The Structure of Ovum
-
Fallopian Tubes and Vagina
-
External Genitalia or Vulva
-
Mammary Glands
-
Transport of Egg and Insemination
-
Hormones Involved During Pregnancy
-
What Is Parturition?
-
Defining Fertilisation
-
Cleavage and Blastocyst Formation
-
Understanding Implantation
-
Placenta – Structure and Function
-
What Is Lactation?
-
Breast Feeding and Its Importance
-
Understanding Oogenesis
-
Menstrual Cycle
-
Ante-Natal Diagnostic Tests
-
Second Week of Development
-
Third Week of Development
-
Disorders Related to Human Reproduction
-
Introduction to Reproductive Health
-
Maternity and Child Health Programme
-
Issues, Requirements and Benefits of Awareness Programme
-
Population Explosion
-
Natural Methods of Birth Control
-
Barrier Methods of Birth Control
-
Hormonal and Surgical Methods of Birth Control
-
Medical Termination of Pregnancy
-
STDs – Syphilis, Trichomoniasis and Hepatitis
-
STDs – Gonorrhoea and Genital Herpes
-
Infertility in Men and Women
-
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
-
Monohybrid Cross
-
Practice Problems on Monohybrid Cross
-
Laws of Mendel – Dominance, Segregation
-
Incomplete Dominance
-
What Is Codominance?
-
Practice Questions on Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
-
Dihybrid Cross and Law of Independent Assortment
-
Practice Questions on Dihybrid Cross
-
Test Cross and Backcross – Monohybrid and Dihybrid
-
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
-
Experimental Verification of Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
-
Crossing Over and Recombination in Inheritance of Gene
-
Genetic Linkage
-
Types of Linkage
-
Genetic Map and Detection of Linkage
-
Polygenic Inheritance and Pleiotropism
-
Multiple Allelism and Its Examples
-
Understanding Epistasis
-
Complementary Gene and Supplementary Gene
-
Mechanism of Sex Determination – Different Methods
-
Sex-Linked Inheritance
-
Mutations – Point Mutation
-
Mutations – Structural Chromosomal Mutation
-
Numerical Chromosome Disorders – Euploidy and Aneuploidy
-
Autosomal Dominant Mendelian Disorders
-
Mendelian Disorders – Autosomal Dominant
-
Autosomal Recessive Mendelian Disorders
-
Sex-Linked Mendelian Disorders
-
Pedigree Analysis
-
Problems on Pedigree Analysis
-
Nucleic Acid Structure
-
Structure of DNA
-
Process of DNA Packaging
-
Search for Genetic Material – Griffith Experiment
-
DNA Is the Genetic Material – The Hershey-Chase Experiment
-
Models of DNA Replication
-
The Meselson-Stahl Experiment
-
Machinery of DNA Replication
-
Mechanism of DNA Replication
-
Difference Between Eukaryotic Replication and Prokaryotic Replication
-
Introduction to Transcription and Transcription Unit
-
Process of Transcription – Prokaryotes
-
Process of Transcription – Eukaryotes and RNA Processing
-
RNA and Its Types
-
Structure of mRNA – Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
-
Structure of tRNA – Adaptor Molecule
-
Genetic Code and Its Discovery
-
Genetic Code, Role of tRNA and the Wobble Hypothesis
-
Introduction to Translation and Structure of Ribosomes
-
Initiation of Translation in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
-
Elongation and Termination of Translation
-
Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
-
Operon Concept and Lac Operon
-
Genome, HGP
-
DNA Fingerprinting – Introduction
-
DNA Fingerprinting – Method and Applications
-
Introduction to Evolution
-
Evolution and Big Bang Theory
-
Theories of Origin of Life
-
Chemical Evolution
-
Biological Evolution
-
Oxygen Evolution and Evidences in Favour of Chemical Evolution
-
Paleontological Evidences of Evolution
-
Archaeopteryx and Pedigree of Evolution
-
Geological Time Scale
-
Homology and Analogy
-
Adaptive Divergence and Adaptive Convergence
-
Evidences From Vestigial Organs, Atavistic Features and Connecting Links
-
Lamarck’s Theory and Weismann's Theory
-
Evidences of Organic Evolution From Embryology and Biogeography
-
Theory of Natural Selection
-
Neo-Darwinism
-
Genetic Drift
-
Examples of Natural Selection
-
Genetic Basis of Adaption, Lederberg Experiment and Types of Natural Selection
-
Speciation and Mimicry
-
Types of Evolution and Reproductive Isolation
-
Similarities and Differences Between Apes and Humans
-
Dryopithecus and Australopithecus
-
Pre-Historic Man – Homo habilis and Homo erectus
-
Homo sapiens – Neanderthal, Cro-Magnon and Modern Man
-
Evolution of Plants
-
A Brief Account of Evolution as a Whole
-
Evolution of Animals
-
Fossil Records and Hardy-Weinberg Principle
-
Introduction to Human Health and Diseases
-
Disease and Its Classification
-
Bacterial Diseases – Typhoid Fever and Tuberculosis
-
Bacterial Diseases – Diphtheria, Pneumonia, Cholera and Plague
-
Viral Diseases – Common Cold, Influenza, Measles, Mumps and Chicken Pox
-
Viral Diseases – Dengue, Chikungunya
-
Fungal Diseases – Ringworm, Candidiasis
-
Helminth Diseases – Ascariasis
-
Helminth Diseases – Filariasis
-
Immunity and Its Types
-
Innate Immunity
-
Protozoan Diseases – Amoebiasis
-
Acquired Immunity – Humoral Immune Response
-
Antigen – Antibody
-
Cell-Mediated Immunity
-
Active Immunisation
-
Passive Immunisation
-
Allergy and Its Types
-
Understanding Autoimmunity
-
Primary Lymphoid Organs
-
Secondary Lymphoid Organs
-
Cancer – Properties of Cancer Cells and Types of Tumours
-
Cause of Cancer and Its Types
-
Cancer – Diagnosis and Treatment
-
Types of Drugs and Adolescents
-
Effects of Drug Abuse and Prevention
-
AIDS and HIV – I
-
AIDS and HIV – II
-
Introduction to Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
-
Animal Husbandry and Dairy Farm Management
-
Poultry Farm Management
-
Animal Breeding
-
Types of Breeding
-
Controlled Breeding Experiments
-
Learning About Beekeeping
-
What Are Fisheries?
-
Plant Breeding and Its Goals
-
Steps of Plant Breeding
-
Plant Breeding for Improvement of Yield
-
Plant Breeding for Disease Resistance
-
Plant Breeding for Pest Resistance
-
Plant Breeding for Improved Food Quality
-
Single Cell Protein
-
Plant Tissue Culture
-
Types of Plant Tissue Culture
-
Somatic Hybridization
-
Application of Plant Tissue Culture
-
Microbes in Human Welfare – Introduction
-
Microbes in the Formation of Curd and Dough
-
Fermented Beverages
-
Microorganisms – Toddy and Cheese
-
Microorganisms in Antibiotics
-
Microbes in Chemicals, Enzymes and Other Bioactive Molecules
-
Microbes in Sewage Treatment
-
Microbes in Biogas Production
-
Understanding Bioherbicide
-
Understanding Bioinsecticide
-
Microbes As Biofertilizers
-
Integrated Pest Management
-
Some Important Biofertilizers
-
Basics of Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA Technology
-
Restriction Enzyme and Their Mechanism of Action
-
Types and Nomenclature of Restriction Enzyme
-
Other Tools for Creating Recombinant DNA – Ligase, Linkers, Adaptors and Homopolymers
-
Features of a Typical Cloning Vector
-
Cloning Vectors – Plasmids
-
Cloning Vectors – Bacteriophages
-
Some Other Cloning Vectors
-
Cloning Vectors in Plants
-
Isolation of DNA
-
Separation and Isolation of DNA Fragments – Gel Electrophoresis
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
-
Transformation in Competent Host – Chemical Methods
-
Transformation in Competent Host – Physical Methods
-
Selection of Transformed Cells
-
Recombinant Protein, Types and Uses and Downstream Processing
-
Bioreactors and Their Types
-
cDNA and Synthetic DNA
-
Pollution, Air Pollution and Air Pollutants
-
Control of Air Pollution
-
Case Study on Air Pollution
-
Noise Pollution
-
Water Pollution – Causes and Effects
-
Biological Oxygen Demand, Chemical Oxygen Demand and Eutrophication
-
What Is Biomagnification?
-
Control of Water Pollution
-
A Case Study of the Integrated Waste Water Treatment
-
Solid Waste and Its Types
-
Solid Waste Management
-
Case Study on the Remedy for Plastic Wastes
-
Agrochemicals, Effects, Case Study of Organic Farming
-
Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
-
Ozone Depletion
-
Radioactive Waste, Deforestation and Improper Resource Utilisation
-
Case Study of the People’s Participation in Conservation of Forests